On-page SEO is optimizing individual web pages to rank higher in search results and attract more relevant traffic. It involves fine-tuning elements like keywords, meta descriptions, headings, and site speed—all critical for boosting visibility and user engagement. A detailed checklist ensures no essential aspect is missed, helping you achieve a fully optimized page. This guide covers every process step, from enhancing content quality to improving user experience, making it easy to effectively elevate your on-page SEO strategy.
Why Is On-Page SEO Important?

On-page SEO ensures your website is optimized for search engines and users. Optimizing various elements on your webpage, such as content, title tag, meta descriptions, URL structure, headings, and images, improves visibility and relevance in search engine results. Focusing on on-page SEO enhances your website’s ability to rank higher in search results, attract more organic traffic, and provide a better user experience.
On-page SEO helps search engines better understand your content, making it easier to index and rank your pages appropriately. Effective on-page SEO boosts your website’s search engine performance and ensures visitors have a seamless, engaging, and informative experience, leading to higher satisfaction and increased conversions.
Keyword Research and Targeting
Keyword research is the foundation of on-page SEO. Choosing keywords that reflect what users are searching for and align with your content goals is essential. With the right keywords, you’ll drive quality traffic that’s interested in your site. Let’s go through each step.
Identify Target Keywords
Begin by finding high-impact keywords—words and phrases that are frequently searched by your target audience. These are the terms that best match your content topic and goals, as they’ll help your page rank higher in search results.
- Use Keyword Research Tools: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find relevant keywords.
- Analyze Search Volume and Competition: Look for keywords with a good balance of search volume (to attract traffic) and low to moderate competition (to make ranking easier).
- Understand Search Intent: Ensure the keywords align with the user’s intent, whether they’re seeking information, a product, or a specific website.
Find Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases often used by people further along in the buying journey or with specific questions. They’re less competitive but highly targeted, making them great for capturing niche audiences.
- Advantages of Long-Tail Keywords: Higher conversion rates because they attract users who know exactly what they’re looking for.
- How to Find Them: Use keyword tools, “People Also Ask” sections, and autocomplete suggestions on search engines.
- Incorporate Naturally: Use these keywords in your content without overstuffing, aiming for a natural flow that answers user questions.
Title Tags/Meta Titles: Crafting the Perfect First Impression
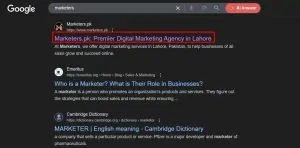
Title tags, or meta titles, are among the most important elements for on-page SEO. These appear as clickable headlines in search engine results, making them the first user interaction with your page. An optimized title tag boosts rankings and encourages users to click through to your site. Here’s how to create powerful title tags:
- Optimize Title Tags: Write unique, descriptive titles for each page. A good title tag should communicate the page’s content, align with user intent, and encourage users to click. Avoid generic or repetitive titles; each should add value to your site’s overall structure.
- Incorporate Target Keywords: Always include your primary keyword naturally within the title. Place the keyword toward the beginning of the title, as search engines give more weight to earlier keywords.
- Character Limit and Best Practices: Keep title tags within 50–60 characters to ensure they display fully on search engine results pages (SERPs). Too long, and the title may get cut off; too short, and it may lack the detail needed to attract users. Avoid “stuffing” keywords, which can lower readability and hurt your SEO.
Meta Descriptions: Crafting Click-Worthy Summaries
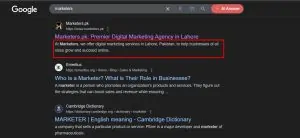
The meta description is the short paragraph displayed under the title tag on search engine results pages (SERPs). While it doesn’t directly impact rankings, a compelling meta description can significantly increase click-through rates. This summary should entice users to visit your page by providing a quick, engaging preview of your content. Here’s how to create effective meta descriptions:
- Writing an Effective Meta Description: Focus on writing clear, persuasive descriptions that give users a reason to click. Think of it as your “sales pitch” for the page, providing just enough information to make the content appealing without revealing everything.
- Include Relevant Keywords: Adding keywords to your meta description helps search engines understand the page’s content and relevance. While keywords in meta descriptions don’t directly influence rankings, bolded keywords in search results can attract users’ attention, increasing the likelihood of clicks.
- Character Limit: Keep descriptions within 150–160 characters to ensure they display fully on SERPs. A concise, well-phrased description gives users enough context to understand the page’s purpose without overwhelming them with information.
URL Structure: The Foundation of On-Page SEO

A well-optimized URL is key for search engines and users, providing a clear and concise path to your content. Creating links that are easy to read and include target keywords helps improve click-through rates and overall site ranking. Here’s how to structure URLs for effective SEO:
- Optimizing URLs: Keep URLs short, straightforward, and descriptive. This means eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on terms that tell users (and search engines) exactly what the page is about. Always try to include the target keyword naturally.
- Avoid Special Characters: Replace spaces and underscores with hyphens (e.g., “your-site.com/seo-guide” instead of “your-site.com/seo_guide”) and avoid using special characters like &, %, $, etc., which can create confusion and errors.
- Consistency in URLs: Maintain a uniform style across your website. For example, if you use lowercase letters in URLs, keep that consistent. This makes your URLs more professional, predictable, and user-friendly, and it’s easier for search engines to index your pages accurately.
Canonical Tags: Avoiding Duplicate Content Issues
Canonical tags are essential for managing duplicate content on your site. When multiple pages have similar or identical content, canonical tags help specify the preferred version, guiding search engines to avoid indexing duplicates. Here’s how to implement canonical tags effectively:
- Use Canonical Tags for Duplicate Content: If you have several URLs with similar content (e.g., category pages or filtered pages), add a canonical tag to the main version you want to rank. This tells search engines which page to prioritize and prevents diluting your SEO value across duplicates.
- Implement Across Similar Pages: Ensure every page with duplicate or similar content includes a canonical tag pointing to the preferred URL. Consistent use of canonical tags across your site can improve overall SEO by consolidating link equity to the main page.
- Self-Referencing Canonicals: Adding a self-referencing canonical tag (pointing to itself) is a best practice, even on pages with unique content. This helps avoid accidental duplication and ensures each page’s URL is indicated as the primary version.
Hreflang Tags: Reaching a Global Audience with Local Relevance
If your site targets users across different countries or languages, implementing hreflang tags is critical. Hreflang tags help search engines serve the correct version of your content to users based on their language and region, improving user experience and SEO. Here’s how to use hreflang effectively:
- Specify Language and Region: Use hreflang tags to indicate language (e.g., en for English) and region (e.g., en-GB for British English, en-US for American English). This helps search engines serve the right content to users based on their location and language preference.
- Create Versions for Different Languages or Regions: For pages targeting multiple regions or languages, ensure you have separate versions and apply hreflang tags to each. This prevents duplicate content issues and enhances relevancy for users in specific locations.
- Use in Conjunction with Canonical Tags: When using hreflang, always add canonical tags to specify the preferred URL for each language/region version. This combination helps avoid conflicting signals for search engines and ensures clear indexing.
Headings (H1, H2, H3…): Structuring Content for Readability and SEO

Header tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are essential for organizing your content in a clear, hierarchical structure, helping both users and search engines understand the importance of each section. Proper use of headings enhances readability and can improve SEO by naturally incorporating keywords. Here’s how to structure content effectively with header tags:
- Structure Content with Heading Tags: Think of headings as a table of contents. Use them to segment your content logically, with H1 as the main heading, followed by H2, H3, and so on to organize subtopics. This hierarchy helps readers easily scan the content and find what they’re looking for.
- Primary Keyword in H1: The H1 tag should be the main title of the page, unique to each page, and contain the primary keyword. This tells both users and search engines what the main topic of the page is. Remember, each page should have only one H1 tag for clarity.
- Secondary Keywords in Subheadings (H2, H3): Use H2 and H3 tags to divide content into sections and include secondary and long-tail keywords where relevant. This makes content more scannable and increases the chances of ranking for related terms.
Content Quality and Relevancy: Engaging Users and Improving SEO
High-quality, relevant content is at the core of effective on-page SEO. Creating content that provides value to users not only keeps them engaged but also signals to search engines that your page is a reliable resource. Here’s how to ensure your content meets both user expectations and SEO standards:
- Write High-Quality, Engaging Content: Provide clear, useful, and well-researched information that directly answers user queries. Aim to create content that stands out for its depth, clarity, and value, as this improves user engagement and time spent on the page.
- Incorporate Keywords Naturally: Organize your primary and secondary keywords within the content. Avoid overusing keywords (keyword stuffing), as it disrupts the flow and can negatively impact rankings. Aim for seamless integration that enhances, rather than detracts from, readability.
- Length and Depth of Content: Content length should align with the topic and user intent. Long-form content tends to rank well, especially when it provides in-depth information. However, the focus should be on quality over quantity—make sure each section adds value.
- Include Outbound Links: Link to authoritative sources or related websites to add credibility to your content. Outbound links show search engines that you’re providing valuable context and enhancing the user experience with reliable resources.
Keyword Placement and Density
Once you’ve identified your target and long-tail keywords, it’s time to incorporate them into your content. Placement matters—put keywords in places where search engines and users look for relevance, like the title, headers, and intro.
- Title Tag and H1: For immediate relevance, include your primary keyword in the title and main heading (H1).
- Introduction and Conclusion: Mention your primary keyword naturally within the first 100 words and near the end.
- Subheadings (H2, H3): Use secondary or long-tail keywords in subheadings where relevant.
Internal Linking: Building a Logical Pathway for Users and Search Engines

Internal linking connects various pages on your website, helping users and search engines navigate your content. A strategic internal linking structure improves user experience, keeps users on your site longer, and helps distribute page authority. Here’s how to optimize internal linking for SEO:
- Strategic Internal Links: Create a logical link structure that guides users to relevant pages. Link to pages that add value or provide more in-depth information, helping users find additional resources without leaving your site. This also helps search engines understand the relationship between pages and their importance within your site.
- Anchor Text Optimization: Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text for your internal links. Instead of generic terms like “click here,” use anchor text that clearly describes the destination page, incorporating keywords when possible. This helps search engines better understand the context of the linked page.
Page Design: Structuring a User-Friendly, SEO-Optimized Layout
A well-thought-out page design is essential for both SEO and user experience. An intuitive, visually appealing design keeps users engaged, reduces bounce rates, and helps search engines understand the content hierarchy. Page design involves organizing your content in a way that’s easy to navigate and encourages interaction. Here’s how to design a page with SEO and user-friendliness in mind:
- Clear and Logical Structure: Arrange your page content in a clear, logical flow that guides users from one section to the next. Use headings, subheadings, and visual cues to break down information into digestible parts.
- Mobile-Friendly and Responsive Design: Ensure your design adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes, especially mobile. Google uses mobile-first indexing, so a mobile-friendly design directly impacts rankings and user satisfaction.
- Optimize Visual Elements: Add images, videos, and graphics that enhance the content without overwhelming the page. Balance aesthetics with functionality, ensuring visuals support the message and load quickly to keep users engaged.
- Focus on Readability: Choose fonts, colors, and layouts that are easy on the eyes. Use ample white space to give the content room to breathe, and break up text with bullet points or short paragraphs.
- Prominent Call-to-Actions (CTAs): Strategically place CTAs that are easy to find and understand. Clear CTAs help users navigate the next steps, whether it’s reading more content, signing up, or making a purchase.
Optimize Images: Enhancing Visuals for SEO and User Experience
Optimizing images is crucial for page speed, accessibility, and SEO. Properly optimized images improve loading times, contribute to a positive user experience, and provide additional context for search engines. Here’s how to get the most out of your images:
- Specify Width and Height: Define the width and height for each image to prevent cumulative layout shift (CLS) and improve page stability. This helps browsers allocate space for images before loading, enhancing user experience and page speed metrics.
- Use WebP Format: Convert images to the WebP format to reduce file size without sacrificing quality. WebP images load faster than traditional formats like JPEG and PNG, improving page speed and better SEO performance.
- Alt Text Optimization: Add clear, descriptive alt text for each image, including keywords where relevant. Alt text provides a textual description of the image for visually impaired users and helps search engines index your images more accurately. Avoid keyword stuffing; focus on describing the image naturally.
- Image Compression: Compress images to reduce file sizes and improve page loading speeds without compromising quality. Use tools or plugins to compress images before uploading them, especially if your site has a lot of media. Faster loading times enhance user experience and SEO performance.
Optimizing Crawlability, Sitemap, and Robots.txt: Ensuring Your Site is Accessible to Search Engines
Optimizing crawlability and using a sitemap is essential for helping search engines efficiently discover and index your pages. A well-structured site with no crawling errors ensures your content is readily accessible, contributing to improved search engine rankings. Here’s how to optimize crawlability:
- Create and Submit a Sitemap: A sitemap is a roadmap for search engines, listing all the important pages on your website. Submit your sitemap through Google Search Console (and Bing Webmaster Tools) to help search engines discover and index your content faster, especially for larger sites or sites with complex structures.
- Check for Crawl Errors: Regularly monitor the webmaster tools/search console for crawl errors that might prevent search engines from accessing certain pages. Resolving these errors promptly helps maintain a smooth crawling process and ensures all important pages are indexed.
- Optimize Robots.txt: Your robots.txt file controls which pages search engines can or cannot crawl. Ensure that essential pages are accessible and irrelevant or sensitive (like login or admin) are blocked. Be cautious with disallowing pages, as blocking important content can negatively affect your SEO.
Schema Markup: Using Structured Data for Enhanced Search Visibility
Schema markup is a powerful tool that adds context to your content, allowing search engines to display richer, more detailed search results. This structured data helps improve click-through rates by making your listings stand out with features like star ratings, FAQs, and product details. Here’s how to effectively use schema markup:
- Add Structured Data: Implement schema markup on key pages (product, service, and FAQ) to enhance search visibility. Structured data provides search engines with detailed information, helping them display rich snippets that are more attractive and informative to users.
- Types of Schema Markup: Choose schema types based on the page’s content. Common types include:
- FAQ Schema: For frequently asked questions, provide users with answers directly in search results.
- Product Schema: For product pages, displaying information like price, availability, and reviews.
- Review Schema: For pages with user reviews or ratings, which can be displayed as star ratings in search results.
- Testing Schema Markup: Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test or the Schema Markup Validator to verify that your structured data is correctly implemented. Regular testing ensures that your markup is error-free and compliant with search engine guidelines, maximizing its impact.
Page Speed Optimization: Enhancing User Experience and SEO Performance
Page speed is crucial for both user satisfaction and SEO, as slow-loading pages can lead to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. Optimizing page speed improves user experience across devices, particularly on mobile, where quick load times are essential. Here’s how to improve page speed effectively:
- Improving Site and Page Speed: Use techniques like caching, compressing images and videos, and minimizing unnecessary JavaScript and CSS files. These tactics reduce load times by cutting down on the amount of data that needs to be processed.
- Minimize Redirects and Use Browser Caching: Redirects add extra steps to loading a page, so limit their use where possible. Implement browser caching to store frequently accessed files, reducing load times for returning visitors by allowing their browsers to load cached resources instead of downloading them again.
- Mobile Page Speed: Given that mobile search has surpassed desktop, ensure all speed optimizations are applied to the mobile version of your site. Tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights can help identify mobile-specific speed issues, allowing you to address them for a better mobile user experience.
Site Audit: A Comprehensive Check-Up for On-Page SEO
A site audit is a crucial component of on-page SEO, as it helps you identify and address any issues that could hinder your site’s performance or visibility. By conducting a regular audit, you ensure your site remains technically sound, user-friendly, and optimized for search engines. Here’s what to focus on in a site audit:
- Technical SEO Check: Identify and resolve technical issues, such as crawl errors, broken links, or missing sitemaps. Use tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs to detect and fix these issues, ensuring search engines can crawl and index your site efficiently.
- Content Review: Assess content across the site to ensure it’s valuable, up-to-date, and optimized with target keywords. Look for duplicate content, outdated information, or missing meta tags, and make updates as needed.
- SEO Elements Check: Review on-page SEO essentials like title tags, meta descriptions, headings, internal/external linking, and schema markup. Make sure all elements are properly optimized to improve rankings and user engagement.
Conclusion
Mastering on-page SEO is about building a strong foundation that supports both user experience and search engine visibility. By focusing on every detail—from keyword research and URL structure to page speed, internal linking, and user engagement—you create an informative and user-friendly site. Regular audits ensure that all elements remain optimized and up-to-date, adapting to any changes in SEO best practices or user expectations. Following this comprehensive on-page SEO checklist will help drive consistent traffic, improve rankings, and foster a positive experience for every visitor to your site.

