When you search something on Google and see more than just the usual blue links—like direct answers, review stars, image rows, or even local maps—you’re looking at SERP features. These are special elements in Google’s search results designed to provide users with quicker, richer information directly on the results page. From Featured Snippets that give instant answers to Knowledge Panels that highlight key facts, these enhancements significantly change how users interact with search.
For businesses and content creators, showing up in these SERP features can be a game-changer. Why? Because they increase visibility, often appearing above the first organic link, and boost click-through rates by making your content stand out. They also signal to both users and Google that your website is authoritative and well-structured.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are SERP Features?

SERP features, or Search Engine Results Page features, are enhanced elements that Google includes in its results beyond the standard list of blue clickable links. These can take many forms, such as featured snippets, images, maps, reviews, FAQs, and more. Their purpose is to help users find answers faster and more efficiently—often without needing to click through to a website.
In traditional search results, listings were primarily limited to page titles, URLs, and meta descriptions. But with SERP features, the experience is now far more dynamic. For example, a user searching “how to make cold brew coffee” might see a step-by-step featured snippet, a video tutorial carousel, and People Also Ask boxes—all before the standard links appear.
From an SEO perspective, these features are incredibly valuable. They can push your content above competitors, increase engagement, and drive more qualified traffic. In many cases, winning a SERP feature is more impactful than ranking #1 organically because of the added visibility and interactivity.
Example in Action:
Try searching “how to tie a tie” on Google. You’ll likely see a featured snippet with step-by-step instructions, a video panel, and FAQ dropdowns—before any standard website links appear. That’s the power of SERP features in action.
Common Types of SERP Features
Understanding the different types of SERP features is essential if you want to target them strategically in your SEO efforts. Each feature serves a unique purpose and responds to specific user intents. Below are some of the most common SERP features you can optimize for:
- Featured Snippets
These are concise answers pulled directly from a webpage and displayed at the top of Google’s search results. They can appear in paragraph form, numbered or bulleted lists, or tables. They’re often triggered by questions or “how-to” queries.
Example: A list showing “5 ways to save energy at home.” - People Also Ask (PAA)
A collapsible list of related questions that users frequently search. Each dropdown provides a brief answer, usually pulled from different sources. Ranking here improves visibility and builds topical authority.
Tip: Structure your content to answer common follow-up questions. - Site Links
These are internal links to other pages of your website that appear under your homepage listing. They help users navigate directly to key sections like “Contact,” “About Us,” or “Blog.”
Note: Google automatically generates site links based on your site structure. - Image Packs
Displayed in a horizontal row or grid, these showcase relevant images from web pages. They are most common in visual searches, like recipes, designs, or products.
How to rank: Use descriptive alt text, structured data, and image sitemaps. - Video Carousels
A scrollable panel that displays YouTube or embedded video results relevant to the search query. Great for tutorials, reviews, or entertainment content.
Optimise with: Video schema and keyword-rich titles/descriptions. - Local Packs (Map Results)
These show a map and three local business listings related to the search term. They’re essential for brick-and-mortar businesses targeting geographic queries.
Includes: Business name, ratings, hours, and directions. - Top Stories / News Boxes
Displays trending news articles related to the search query, often in a card-style carousel.
Eligibility: Requires publishing timely, relevant content and using the NewsArticle schema. - Knowledge Panels
Rich information boxes appear on the right side of the search results, typically for brands, people, or organisations.
Content source: Wikipedia, Google’s Knowledge Graph, and verified data sources. - FAQS and How-Tos
Structured as expandable dropdowns or step-by-step guides. These appear directly under the search listing if the page is marked up with the appropriate schema.
Good for: Customer support pages, tutorials, and product descriptions.
How Google Chooses SERP Features

Google doesn’t randomly decide which content earns a SERP feature—it uses advanced algorithms to match the search intent with the most useful format and content. Understanding how this works can help you position your site to qualify for these valuable placements.
Role of User Intent and Query Type
Google’s top priority is delivering the most relevant result for a user’s query. That means understanding why someone is searching. For example:
- A “how-to” query may trigger a Featured Snippet or Video Carousel.
- A local service query like “pizza near me” will likely show a Local Pack.
- A question like “Who is Elon Musk?” might trigger a Knowledge Panel.
Different types of queries (informational, navigational, transactional) call for different SERP formats.
• Google Algorithms: RankBrain, BERT, and AI Signals

Google’s decision-making is powered by complex AI-driven algorithms:
- RankBrain helps Google interpret the meaning behind a search, even if the exact words aren’t familiar.
- BERT understands the nuances of natural language, helping to match content with conversational queries.
- These models evaluate the searcher’s intent, phrasing, and context to decide which SERP features should be displayed.
Relevance, Authority, and Structure of Content
To earn a SERP feature, your content must:
- Be highly relevant to the user’s query.
- Come from a trusted source with a strong backlink profile and domain authority.
- Be well-structured, using proper headings, lists, tables, and schema markup.
How to Optimise Content for SERP Features

If you want your content to appear in SERP features, it’s not just about what you say—it’s about how you say it. Google favors content that is clear, well-structured, and easy to understand. Here’s how to optimise your pages to increase your chances of earning these enhanced listings:
• Write Clear, Structured, and Concise Answers
Start by identifying the questions your audience is asking and then provide direct, well-worded answers early in your content. Use short sentences and keep answers under 40–50 words if you’re targeting Featured Snippets.
Example: If someone asks, “What is digital marketing?”, open your blog with a one-paragraph answer before going into deeper details.
• Use Headings, Bullet Points, and Ordered Lists
Break your content into sections with clear H2 and H3 headings. When explaining steps, use numbered (ordered) lists. For feature comparisons or grouped ideas, use bullet points. These formats will likely be pulled into snippets or People Also Ask boxes.
Bonus: Proper formatting also boosts readability for users and accessibility for screen readers.
• Create Step-by-Step Content for How-Tos
Google loves content that walks users through a process, especially in list form. If your topic is instructional (like recipes, setup guides, or DIYs), structure your content as a step-by-step process. Use H3 or <ol> tags with “Step 1, Step 2…” formatting.
Enhance it further: Add HowTo schema to signal the format explicitly.
• Implement “Question-Answer” Formats in FAQS
Adding a dedicated FAQ section at the end of your article (or throughout the page) is a smart way to win space in the FAQ-rich results. Use actual search queries as your questions, and provide honest, concise answers.
Example:
Q: How can I improve my Google search ranking?
A: Focus on content quality, page speed, mobile responsiveness, and backlink strategy.
Add Schema Markup to Enable Rich Results
One of the most effective ways to qualify for SERP features is by adding schema markup, also known as structured data, to your webpages. Schema tells Google more about your content in a machine-readable format, which can unlock rich results like review stars, FAQS, images, breadcrumbs, and even video previews.
What Is Structured Data and Why Does It Matter
Structured data is a standard format (based on schema.org vocabulary) that helps search engines understand your pages’ content and context.
Using schema enables Google to display your content more visually and informatively in search results—leading to better click-through rates, more impressions, and even voice search visibility.
JSON-LD vs Microdata: Which to Use

There are two main ways to implement schema:
- JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) – Recommended by Google; it’s cleaner, faster, and separate from your HTML content.
- Microdata – Embedded directly into HTML tags; harder to manage and less scalable for large websites.
Pro tip: Stick with JSON-LD for simplicity and future-proofing.
Types of Schema You Should Use
Here are the most useful schema types for enabling rich results:
- FAQ Schema – Ideal for question-answer formats, great for SERP dropdowns.
- How-To Schema – For instructional content (with steps and images).
- Article Schema – Used for blogs, news posts, and editorial content.
- Product Schema – Displays product name, price, availability, and ratings.
- Review Schema – Showcases individual or aggregate ratings for services/products.
Example of Properly Implemented FAQ Schema (JSON-LD)
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “What is schema markup?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Schema markup is a code you add to your website to help search engines better understand your content.”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Does structured data improve SEO?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Yes, it helps your content become eligible for rich results, improving visibility and click-through rates.”
}
}
]
}
</script>
Tools to Help You Add Schema Easily
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper – Great for generating markup for your content without coding.
- Rich Results Test – Validate your page’s schema and see which SERP features it qualifies for.
- Schema Pro (WordPress Plugin) – Easily implement schema if you’re using WordPress.
Win Image, Video & News SERP Features
Beyond text, Google displays rich media in its SERPS—images, videos, and news stories—all of which offer high-visibility opportunities for content creators. To rank for these media-based SERP features, you need to optimise your visual content using SEO best practices and structured data.
Optimizing Alt Text, Filenames, and Image Sitemaps
Google relies on image context to understand what a photo represents. To make your images eligible for Image Packs:
- Alt Text: Use descriptive and keyword-rich alt attributes (e.g., alt=”homemade matcha latte in ceramic cup”).
- Filenames: Rename files clearly (e.g., matcha-latte-recipe.jpg, not IMG_0012.jpg).
- Image Sitemaps: Include all important images in your sitemap.xml or a dedicated image sitemap.
These steps help your images appear in Image Packs and Google Images, increasing visibility and traffic potential.
Using Video Schema for YouTube or Hosted Videos
Video content is often pulled into Video Carousels, especially for how-to guides, reviews, and tutorials.
To optimize your video content:
- Use VideoObject schema (JSON-LD) to provide video title, description, duration, thumbnail, and embed URL.
- Host videos on YouTube or ensure proper indexing if self-hosted.
- Include transcripts and timestamps to help with indexing and SERP snippet selection.
Example – Video Schema Snippet:
json
CopyEdit
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “VideoObject”,
“name”: “How to Brew Cold Matcha”,
“description”: “A step-by-step tutorial on making cold matcha at home.”,
“thumbnailUrl”: “https://example.com/thumb.jpg”,
“uploadDate”: “2025-05-01”,
“duration”: “PT3M45S”,
“contentUrl”: “https://example.com/videos/matcha.mp4”,
“embedUrl”: “https://www.youtube.com/embed/xyz123”
}
Creating Newsworthy Content with Proper Metadata for Top Stories
You can appear in Google’s Top Stories box if you publish timely, journalistic content. Requirements include:
- Publishing high-quality, current news or press release content.
- Using the NewsArticle schema for title, author, publish date, and headline.
- Submit your site to the Google News Publisher Centre for indexing.
Include AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages), as Google often favours AMP-enabled content in mobile SERPS.
Embed Examples of Optimised Media
Use visual examples directly in your blog to reinforce your optimisation:
- Show a before/after image of filenames.
- Embed a YouTube video with proper schema beneath.
- Add a screenshot of a page in “Top Stories” or a video carousel.
How to Track SERP Feature Performance

Adding structured data and optimising content is only part of the process—measuring the impact of SERP features is just as important. Tracking your performance helps you understand what’s working, where improvements are needed, and how your visibility compares to competitors.
Use Google Search Console (GSC): Check Impressions, Clicks, CTR
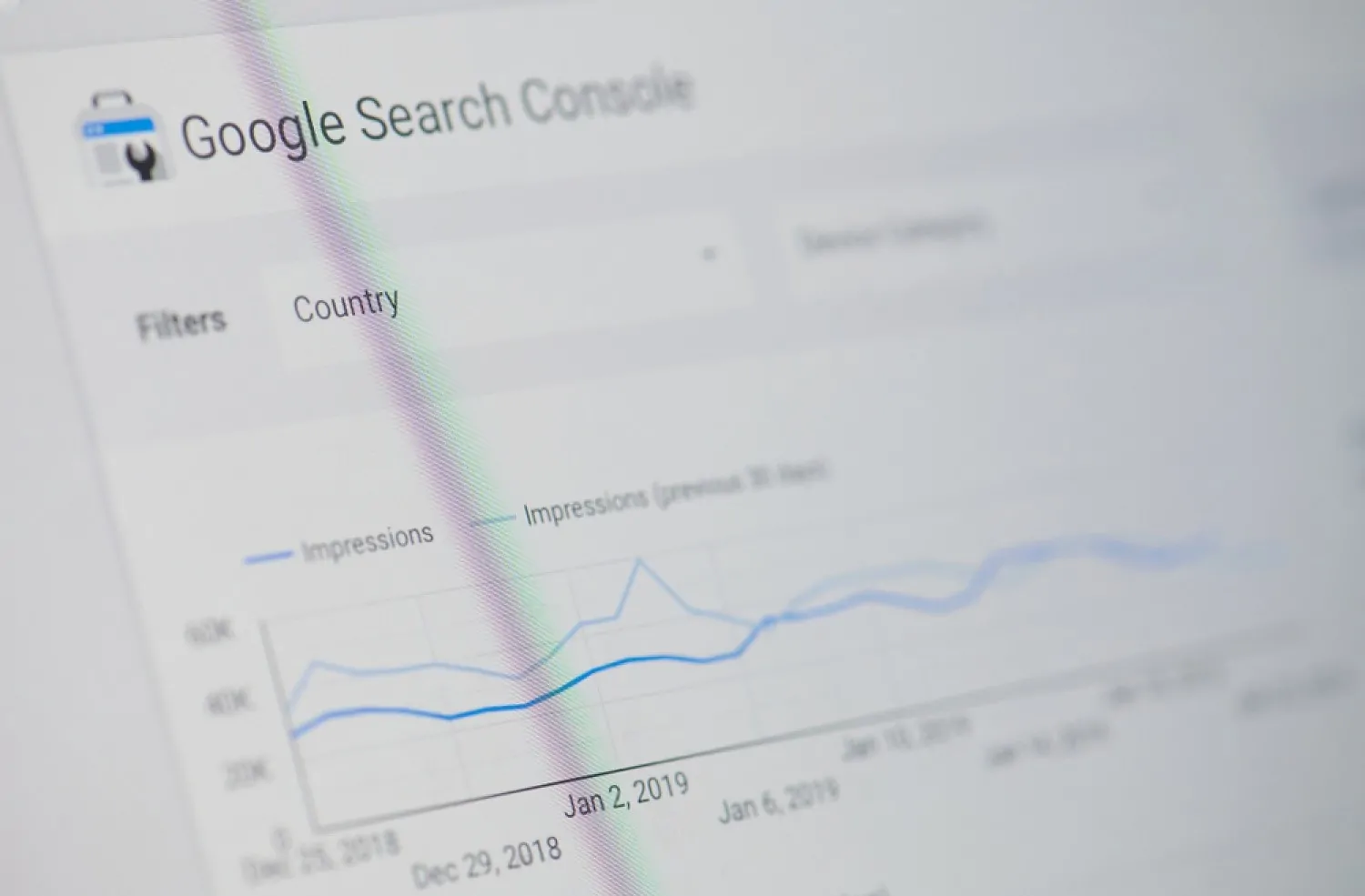
Google Search Console is a free, essential tool for measuring your pages’ performance in organic search. To track SERP features:
- Go to Performance > Search Results.
- Use the “Search Appearance” filter to see how your pages appear with rich results (e.g., FAQ, How-To, etc.).
- Analyse Impressions (how often your page appeared), Clicks, and CTR (Click-through Rate).
Use Tools Like SEMrush or Ahrefs for SERP Feature Tracking
Both SEMrush and Ahrefs provide advanced SERP feature tracking and keyword analytics:
- SEMrush shows which of your tracked keywords trigger SERP features—and whether you’re occupying those slots.
- Ahrefs provides a SERP Overview with details on feature types like featured snippets, People Also Ask, site links, and more.
You can also monitor competitors to see what content or structure earns them the feature spot.
Key Metrics to Monitor
To assess your SERP feature performance, focus on:
- Visibility: Are your URLs appearing in SERP features?
- Position: Are you ranking in position 0 (above #1) or within the top 3?
- Click-through Rate (CTR): Are users clicking on your listing after seeing the feature?
- Search Appearance: What type of enhancements are shown for your content?
Tracking these over time helps determine which content formats and schema types give you the best return—and where to double down or adjust your strategy.
Conclusion
SERP features are a powerful SEO advantage, helping your content stand out with greater visibility, trust, and engagement. From featured snippets to image carousels and FAQ dropdowns, these elements enhance user experience and drive higher click-through rates. To tap into their full potential, focus on well-structured content, use schema markup like JSON-LD, and align your content with search intent. Tools like Google Search Console and SEMrush can help you track performance and refine your strategy. Ultimately, consistent

